Is Creatine Safe for the Heart?
The heart is a highly metabolic organ that relies on a continuous supply of energy to maintain its rhythmic contractions and overall function. Creatine’s role in energy metabolism extends beyond skeletal muscle; it also has implications for cardiac health. The heart utilizes ATP for various functions, including contraction and relaxation cycles, and any disruption in […]
Read More
Can I Workout Daily with Creatine?
The benefits of creatine supplementation for exercise performance are well-documented and supported by numerous scientific studies. One of the most significant advantages is its ability to improve strength and power output during high-intensity training. Athletes who incorporate creatine into their regimen often experience enhanced performance in activities that require short bursts of energy, such as […]
Read More
Should I Stop Taking Creatine?
The benefits of creatine supplementation are well-documented and extend beyond just improved athletic performance. One of the most significant advantages is its ability to enhance strength and power output during resistance training. Numerous studies have shown that individuals who supplement with creatine can lift heavier weights and perform more repetitions compared to those who do […]
Read More
Optimal Creatine Dosage: How Often?
Several factors can influence the optimal dosage of creatine for an individual. One of the primary considerations is body weight. Research suggests that a higher body mass correlates with a greater volume of muscle tissue, which in turn may necessitate a larger creatine intake to achieve saturation levels in the muscles. For example, an athlete […]
Read More
Top Foods High in Creatine: Beef, Salmon, and Pork
Beef is one of the most abundant sources of creatine available in the diet. A typical serving of beef contains approximately 2 to 5 grams of creatine per kilogram of meat. This makes it an excellent choice for individuals looking to boost their creatine intake through natural food sources. The concentration of creatine can vary […]
Read More
Is it safe to take creatine every day?
One of the most well-documented benefits of creatine supplementation is its ability to enhance athletic performance, particularly in high-intensity, short-duration activities. Studies have shown that creatine can increase strength, power output, and muscle mass. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that creatine supplementation significantly improved strength gains […]
Read More
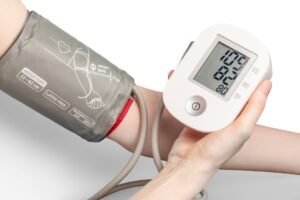
Does Creatine Affect Blood Pressure?
The relationship between creatine supplementation and blood pressure is a topic of growing interest among researchers and healthcare professionals. Blood pressure is a critical indicator of cardiovascular health, with elevated levels being a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. While creatine is primarily associated with muscle performance, its effects on the cardiovascular system […]
Read More
The Impact of Creatine on Hair Loss: What You Need to Know
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a potent androgen hormone derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. DHT plays a significant role in the development of male characteristics and is also implicated in various physiological processes, including hair growth. However, elevated levels of DHT are often associated with androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male […]
Read More
The Impact of Creatine on Heart Health
The relationship between creatine and heart health is an area of growing interest among researchers and healthcare professionals. The heart relies heavily on ATP for its contractile function, making creatine an essential component in maintaining cardiac energy homeostasis. In conditions where the heart’s energy demands are increased or its supply is compromised, such as in […]
Read More
Is Creatine Safe for the Kidneys?
Creatine is stored primarily in skeletal muscle, where it exists in two forms: free creatine and phosphocreatine. The latter is crucial for the rapid regeneration of ATP during high-intensity exercise. When a muscle contracts, ATP is broken down into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate, leading to a temporary energy deficit. Phosphocreatine donates its phosphate […]
Read More